System Restore is one of the best ways to keep your system ready to face any kind of issues which may happen during application installation or system updates. System Restore feature on new Windows systems basically creates copies of files before system changes happen and manually by the user. This happens for instance when you install a new driver or update Windows.
Total System Restore file size depends on the hao many drives you are adding or the amount of the data on the system, however, it can be managed by doing system restore on individual drives, or turn it off completely, via Control Panel > System and Security > System > Advanced system settings > System Protection. A click on configure in the menu opens the system restore preferences for the selected drive. Here you can reduce or increase the size available to the feature, or turn it off completely for the drive.
How to Manage System Restore From the Command Line?
By default, it won’t allow you to delete the System Restore point but you can use the System Restore Manager to delete individual points to free up room on the hard drive. If you want to avoid the third party installation then you can also do it from the command line.
Open an elevated command prompt.
- Windows 7: click on the start menu, then All Programs > Accessories. Right-click Command Prompt and select Run as Administrator from the context menu.
- Windows 8: Tap on the Windows-key to open the start page. Enter cmd here, right-click on the Command Prompt result, and select Run as Administrator from the bottom toolbar.
Commands
-
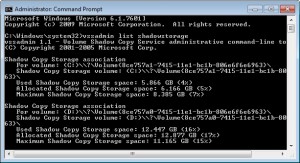
vssadmin list shadowstorage
- Above command lists all connected hard drives and their use, allocated and maximum shadow copy storage space.
-
vssadmin list shadows
- Above command lists all existing shadow copies on the system
-
vssadmin delete shadows /for=c: /oldest
- Above command deletes the oldest shadow copy on drive C
-
vssadmin delete shadows /for=d: /all
- Above command deletes all existing shadow copies on drive D
-
vssadmin delete shadows /for=c: /shadow=ID
- Deletes the selected shadow copy. The IDs are listed when you use the list shadows command.
-
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=c: /maxsize=2GB
- Sets the shadow storage for drive C to 2 Gigabyte. May delete existing restore points starting with the oldest if space is not sufficient to store all System Restore points
Related Posts:
How to Restore System with “System Restore Point”
How to Create System Restore Point on Windows 7
How to Backup and Restore System on Windows 8